In fact, the working principle of gas generator sets and coal-fired generator sets is the same. The main difference is that coal-fired power plants use boilers to burn coal, generate steam to drive the turbine, which then drives the generator. Gas generator sets, on the other hand, burn gas directly in the turbine to do work, drive the gas turbine to rotate, and then drive the generator. Although both are generating electricity, the power to drive the generator to generate electricity is different
Generally speaking, there are relatively few auxiliary systems for gas generator sets, so both gas turbines and generators are containerized, which shortens the construction cycle of gas generator sets. However, the auxiliary systems for coal-fired generator sets are relatively large, with many fans, pumps, fuel (coal) systems, and so on surrounding the boiler and steam turbine. Moreover, the cost of gas turbine wheels is higher than that of coal-fired power plants
Similarly, for power generation units, the difference in fuel creates the difference in the unit. After all, the fuel is fixed and the unit revolves around the fuel. Therefore, the working principles of different power generation units are different, resulting in differences in the price of power generation units
1. Single phase grounding protection is a single-phase grounding protection for the stator winding of a generator.
2. Low excitation and loss of excitation protection is required to prevent large generators from absorbing a large amount of reactive power from the system after the excitation current is below the static stability limit or the excitation current is lost to zero, which can have adverse effects on the system. Generators with a capacity of 120MW and above must be equipped with this protection.
3. Longitudinal differential protection for inter phase short circuit protection of stator winding and outgoing line.
4. The grounding protection of the excitation circuit is the grounding fault protection of the excitation circuit.
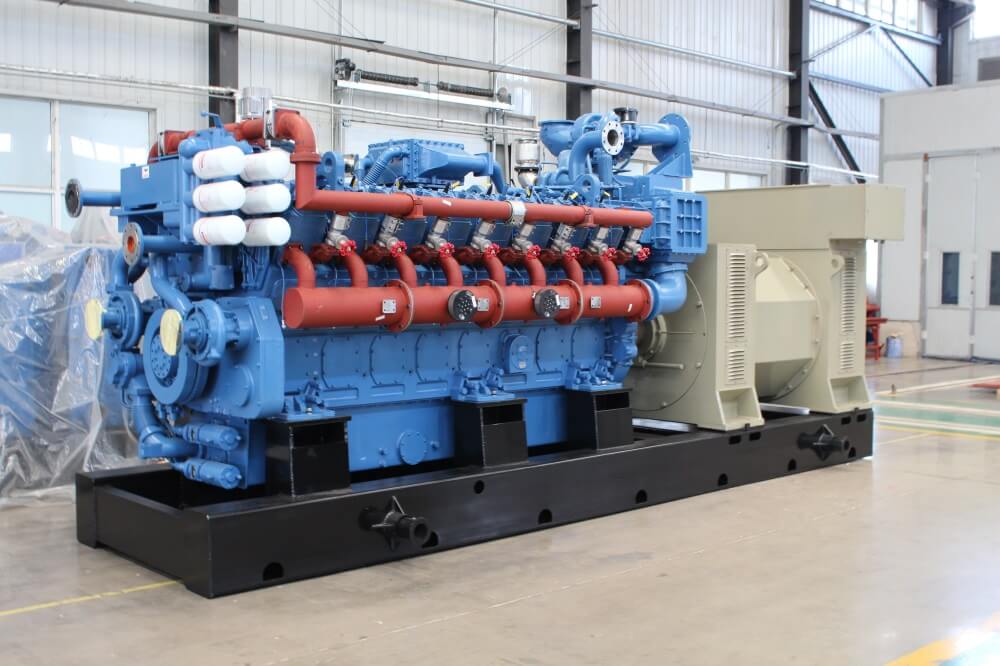

5. The transverse differential protection is used for the protection of one phase inter turn short circuit in the stator winding.
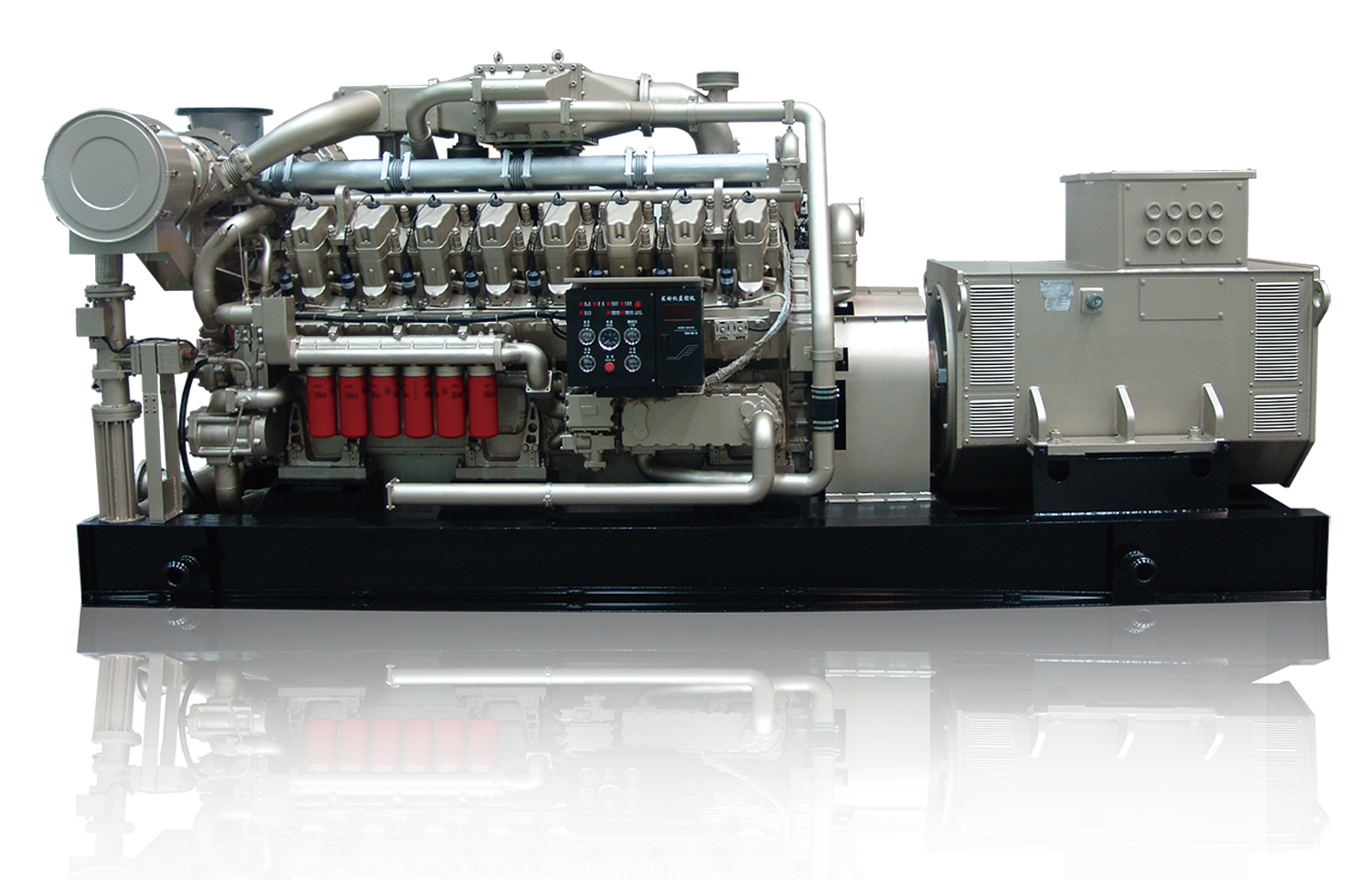
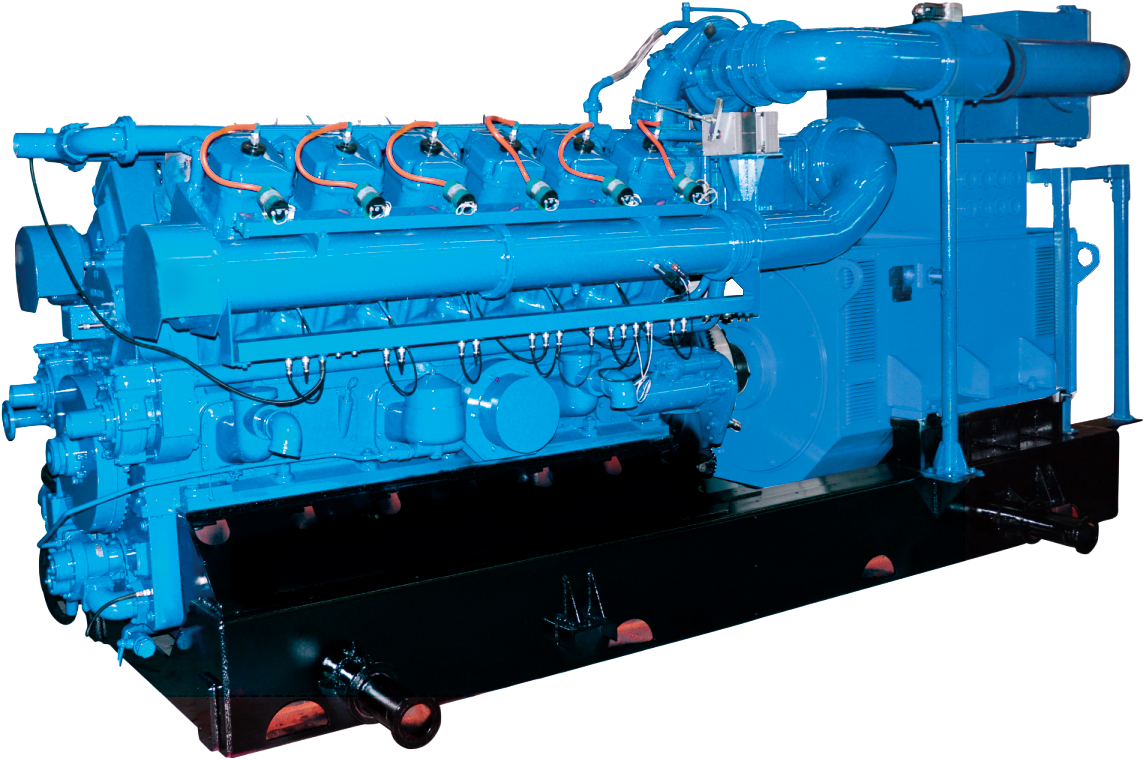
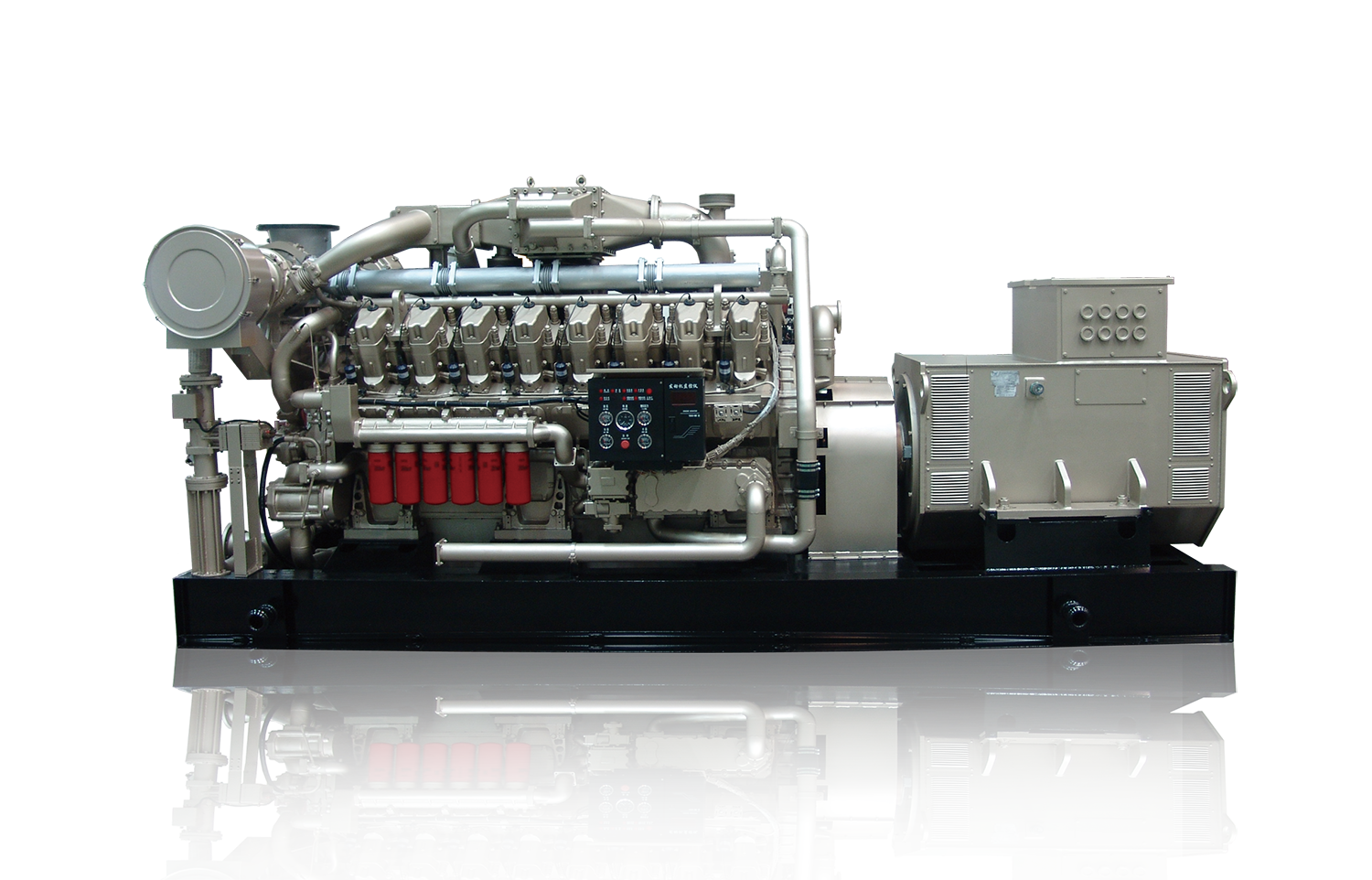
40KW50KVA natural gas generator unit Price of natural gas generator unit
6. Overload protection: Small and medium-sized generators are only equipped with set point overload protection; Large generators should be equipped with stator overload and excitation winding overload protection separately.
7. Stator winding overcurrent protection: When a short circuit occurs outside the range of generator longitudinal differential protection, the protection of the short-circuit component and the circuit breaker refuse to act. This protection is a backup for external short circuits and also a backup protection for longitudinal differential protection.
8. Out of step protection reflects the out of step protection of large generators and system oscillation processes.
9. Negative sequence current protection: When asymmetric short circuits and three-phase loads occur in the power system, such as electric locomotives, electric arc furnaces, etc., when the proportion of single-phase loads is too large, it can cause overheating at the rotor end, inner surface of the protective ring, and other places with high current density, causing local burns. Therefore, negative sequence current protection should be installed.
10. Stator winding overvoltage protection prevents stator winding overvoltage caused by sudden shedding of all loads. Both hydro generators and large turbine generators must be equipped with overvoltage protection, while small and medium-sized turbine generators are usually not equipped with overvoltage protection.




 Tel:0531-69953988
Tel:0531-69953988  Add:101, Building 5, Liandong U Valley Science and Technology Innovation Center, Zhangjin Comprehensive Bonded Zone, No. 33688 Jingshi East Road, Suncun Street, Jinan Area, China (Shandong) Pilot Free Trade Zone
Add:101, Building 5, Liandong U Valley Science and Technology Innovation Center, Zhangjin Comprehensive Bonded Zone, No. 33688 Jingshi East Road, Suncun Street, Jinan Area, China (Shandong) Pilot Free Trade Zone

